That feeling of your knee “giving out” or throbbing with pain are two very common patient complaints. Your knees work hard, so it’s no surprise either or both react to the workload. There are a myriad of reasons for knee pain and many ways physical therapy (PT) can help improve or resolve it.
Types of Pain
There are three main categories of pain. Acute pain is the severe pain right after an injury. Sub-acute pain can kick in a few weeks after the injury and can last up to six months. Chronic pain is discomfort that lasts past the six-month mark.
Recommended Treatment Response
During the acute period, lean into the RICE treatment, which means rest, ice, compression, and elevation. The goal is to give your knee a chance to heal before asking it to perform movements and carry weight.
During the sub-acute pain period, introduce gentle movement to improve mobility.
Along the way, keep in touch with your medical professionals, who will evaluate your range of motion and pain levels, among other things. They may request imaging if there is concern over damage to muscles, ligaments, tendons, or bones. Chronic pain often persists even after the core issue has been addressed, but if you haven’t already, now is the time for a thorough evaluation and assessment from your medical professional.
At any point along the way, your physician may recommend physical therapy to help improve mobility and rebuild strength.
Types of Knee Injuries
From cartilage wearing down to ligament tears, the knees can suffer a host of injuries such as:
- ACL tear
- PCL injury
- MCL damage
- Osteoarthrosis
- Patellar instability
- Patellofemoral stress syndrome (PFSS)
- Iliotibial band (ITB) stress
- Hamstring strain
- Baker’s cyst
- Bursitis
- Sprains and strains
Symptoms to Watch for
In addition to pain, there are other indicators of knee injury or instability to pay attention to. Seek medical advice if you have symptoms such as locking, catching, or clicking when you bend your knee, a popping sensation when you twist or bend the knee, or an inability to straighten the knee completely.
What to Expect From Your PT Appointment
Your physical therapist will ask a range of questions regarding the initial injury, how long it’s been bothering you, if you’ve had similar issues in the past, what seems to help or exacerbate the problem, and what diagnosis and treatment you’ve already received. 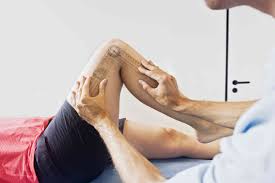
He or she will then test your gait, range of motion, strength, balance, and physical structures of the knee. They will complete a comprehensive assessment of your entire lower extremity from your hips to your feet.
PT Strengthening and Exercise
Although the movements may seem small, physical therapy exercises target the problem area, slowly strengthening muscles and increasing mobility. Your PT will work you through a variety of exercises at your appointment and send additional activities home with you. They may also offer pain-relieving therapies like electric stimulation, kinesiology taping, heat and ice application, soft tissue massage, or bracing.
Your PT can walk you through proper technique for strengthening, mobility, and balance exercises so you can improve without causing further injury.
This might include exercises like:
- Straight leg raises to the front, side, or back
- Exercises to strengthen your hips
- Stretches for targeted muscles in the lower extremities
- Knee lifts
- Hip rotations
- Mini-squats with or without aids
- Hip flexion, extension or abduction exercises
- Hamstring curls
- Hip bridge
- Step exercises
 Working with your physical therapist regarding knee pain and instability can not only improve your current pain level and mobility issues, but can help you maintain the strength and control to avoid strains and injuries in the future. Once your knee instability and pain have improved and you get the green light from your doctor or PT, try low impact activities like yoga, swimming, walking, and tai chi to keep the progress going.
Working with your physical therapist regarding knee pain and instability can not only improve your current pain level and mobility issues, but can help you maintain the strength and control to avoid strains and injuries in the future. Once your knee instability and pain have improved and you get the green light from your doctor or PT, try low impact activities like yoga, swimming, walking, and tai chi to keep the progress going.
To get started, give Encore a call today to see how we can help with your knee pain and instability.
Sources:
https://www.healthline.com/health/types-of-pain
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/injury-knee-pain-16/slideshow-knee-exercises
